lectures
GNSS exam 1
2. Answer Questions.
- What is the “three steps” strategy in the construction of BeiDou statellite system ? 北斗卫星导航系统建设的三个阶段是什么?
第一步,建设北斗一号系统,主要由两个地球静止轨道卫星和一个备份卫星组成;第二部,建设北斗二号系统,实现亚太地区区域卫星导航覆盖;第三步,建设北斗三号系统,实现全球组网。 - How to convert the XYZ coordinate in WGS-84 to the BLH in CGCS2000?如何将WGS-84坐标系下的XYZ坐标转换成CGCS2000的BLH坐标?
先使用布尔莎模型等方法,将WGS-84 XYZ坐标转换成CGCS2000 XYZ坐标,再经过迭代算法将CGCS2000 XYZ坐标转换成CGCS2000 BLH坐标。 - What are the differences between celestial reference system and terrestrial reference system? 天球坐标系和地球坐标系的区别是什么?
天球坐标系用来表示天体相对于地球的位置,而地球坐标系用来表示地面上物体的位置。天球坐标系没有半径的大小,半径背离地球球心无限延申,而地球坐标系以地球半径大小为半径长度。 - How to construct a coordiante reference system and a time referencce system? 如何构建一个坐标参考系和时间参考系
构建坐标参考系: 为了在地球表面确定一个准确的位置,必须要直到地球本身的形状和大小;确定空间参考系的类型;确定地球的原点、基准面(参考椭球)、基准线(坐标轴方向)等。构建时间参考系:(1)确定时间间隔;(2)确定时间的起点。 - What is the relationship among geoid undulation(undulation,起伏,波动),ellipsoid height and ortho height?大地水准面高程、参考椭球高程和垂直高的关系是什么?
大地高:地面点沿椭球面的法线到椭球面的距离;正高:地面点沿铅垂线到大地水准面的垂直距离;正常高:验铅垂线到似大地水准面的垂直距离。大地高=正高+大抵是准面差距;大地高=正常高+高程异常。 - What are the advantages of geocentric ellipsoid comparing to the reference-centric ellipsoid? 地心椭球和参心椭球相比有什么优点?
参心坐标系往往的椭球是选择在一定区域内的大地水准面的最佳拟合,不能够适应研究地球整体的性质和重力场等。使用地心椭球,其球心与地球球心误差很小,能够满足人造地球卫星等全球应用的需要。 - What is pseudo-range? And what are the advantages and disadvantages of pseudo-ranges? 什么是伪距?伪距的优点和缺点?
伪距是GNSS 卫星观测得到的GPS测站到卫星的距离,尚未对卫星和接收机钟差影响进行改正,故称为伪距。卫星按照星载时钟发射某一结构的伪随机噪声码信号,经过时间Δt,到达接收机天线,用Δt乘以光速c就是卫星到接收机的空间距离ρ。一次定位精度不高,但是定位速度块,没有多值性问题。 - Why do we need to perform linear combination of measurements? 为什么要进行线性组合观测?
In GNSS observation, besides the original pseudorange and carrier phase measurements, a large number of virtual measurements formed by linear combination are used to eliminate some unknown parameters and simplify adjustment calculation.在GNSS观测中,除了原始的伪距观测和载波相位观测之外,通过线性组合形成一些虚拟观测方式可以用来消除一些未知参数,简化计算。 - What are the single difference,double dfifference and triple difference? 什么是单差?双差?三差?
单差:同一历元,两台接收机对同一颗卫星相位观测值之差。双差:不同测站上,两个接收机观测两颗卫星p、q,形成两个单差,对两个单差进行组合得到双差。相邻两个历元的双差观测之差构成三差。单差消除了卫星钟差,对流层延迟、电离层延迟误差也得到削弱,基线较短时认为基本消除,还存在接收机钟差。双差消除了接收机钟差。三差消去了整周模糊度。 - How to eliminate ionospheric errors in GNSS observation, please list at least 3 methods? 在GNSS观测中,如何消除电离层误差?至少列举3种方法
(1)电离层延迟与频率有关,使用双频接收机即可消除。(2)使用电离层时延的昼夜变化模型。(3)使用广域差分技术。
3. Very briefly defines the following terms and acronyms(缩写)
-
WAAS
Wide Area Augmentation System,广域增强系统 -
LASS
Local Area System ,局域差分系统 -
NRTK
network real-time kinematic positioning, NRTK 网络实时动态定位 -
GBAS
Ground-based augmentation systems, 地基增强系统 -
SBAS
Satellite-based augmentation systems,星基增强系统 -
Integer ambiguity
整周模糊度 -
NRTK
network real-time kinematic positioning, NRTK 网络实时动态定位 -
VRS
Virtual Reference Station, VRS ,虚拟基准站技术,是一种网络实时动态测量技术 -
Signal modulation
信号调制 -
CDMA
码分多址 -
PRN
pseudo random noise code, PRN, 伪随机噪声码 -
SPS
Standard Positioning Service ,SPS,标准定位服务. Precision Positioning Service, PPS,精密定位服务 -
PPP
Precise Point Positioning, PPP, 精密单点定位 -
Cycle slip
整周跳变,周跳 -
Kepler elements
开普勒轨道参数 -
IGS
International GNSS Service, IGS, 国际GNSS服务 -
Ephemeris
星历,分为广播星历和精密星历 -
Almanac(?)
历书,用于计算任意时刻天空中任意卫星的概略位置。
Difference between Ephemeris & Almanac: GPS接收机收到广播行李(Broadcast Ephemeris)和历书(Almanac)两种导航信息。广播星历包含基本轨道参数及摄动改正量,由其确定的卫星位置精度高,可用于定位计算。历书仅提供基本轨道参数,精度低,可用于接收机快速捕获卫星和预报。
为了缩短卫星锁定时间,GPS接收机要利用历书、当地位置的时间来预报卫星运动状态。历书与星历都是表示卫星运行的参数。历书包括全部卫星的大概位置,用于卫星预报;星历知识预报当前接收机观测到的卫星的精确位置,用于定位。
-
Integrity
完整度 -
PPP
Precise Point Positioning ,PPP, 精密单点定位 -
float solution
浮点解 -
Ratio test
比例检验 -
Simultaneous observation loop
同步观测环 -
Non-simultaneous observation loop
异步观测环 -
Baseline solution
基线解算
4. Application Questions
If you know the coordinates of point A under ITRF2000 on October 10,2012, how to get the coordinates of epoch 2000 (CGCS2000) of that point under framework of ITRF1997 ?
已知点A在ITRF2000 2012年10月10日,如何得到在ITRF1997的2000历元的坐标?
Calculation tips:
- Day of year is 2012.7726(10th Oct,2012);
- The coordinates of point A under ITRF2000 on October 10,2012 are: \(\left \{ \begin{matrix} X(2000/2012.7726)=2, \\ Y(2000/2012.7726)=3, \\ Z(2000/2012.7726)=5, \end{matrix} \right.\)
2012年10月10日表示为2012.7726。
-
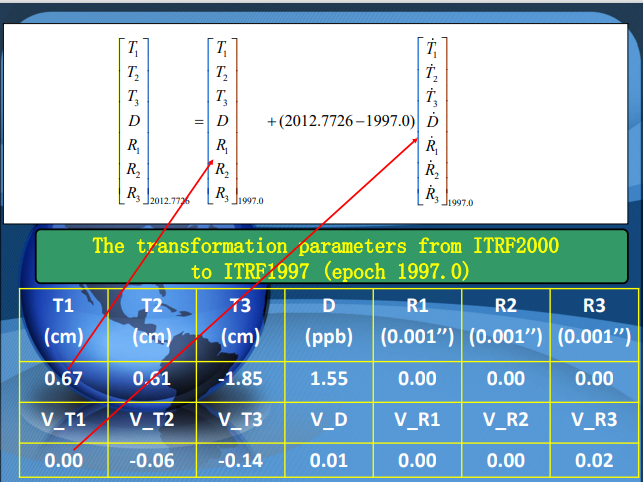
THe conversion parameters from ITRF2000 to ITRF1997 in epoch 1997.0 are: Translation parameters : T1=0.0067,T2=0.0061,T3=0.0185;
Scale parameter: D=1.55;
Rotation parameters: R1=0,R2=0,R3=0; -
THe speed of the above conversion parameters are :
${T_1}=0.0067,{T_2}=0.0061,{T_3}=-0.0185,D=1.55,{R_1}=0,{R_2}=0,{R_3}=0$
$V_{T_1}=0,V_{T_2}=-0.0006,V_{T_3}=-0.0014,V_D=0.01,V_{R_1}=0,V_{R_2}=0,V_{R_3}=0.02$ -
The speed of point A under the framework of ITRF 1997 is :
$V_X=0.002,V_Y=0.001,V_Z=0.003;$ -
The conversion formula for different ITRF framework is:
\(\begin{bmatrix} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{bmatrix}_{_{ITRF_{YY}}}=\begin{bmatrix} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{bmatrix}_{_{ITRF_{XY}}}+\begin{bmatrix} T_1 \\ T_2 \\ T_3 \end{bmatrix}+\begin{bmatrix} D & -R_3 & R_2 \\ R_3 & D & -R_1 \\ -R_2 & R_1 & D \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{bmatrix}_{_{ITRF_{XX}}}\)
THe following three questions need to be answered:
(1) Write out the transformation parameter from ITRF2000 to ITRF1997 at epoch 2012.7726:
\[\begin{matrix} T1_{2012.7726}= & T2_{2012.7726}= & T3_{2012.7726}=& D_{2012.7726}= \\ R1_{2012.7726}= & R2_{2012.7726}= & R3_{2012.7726}= \end{matrix}\](2) The coordinates of point A in ITRF1997 at epoch 2012.7726
X(1997/2012.7726)=
Y(1997/2012.7726)=
Z(1997/2012.7726)=
(3) Please write out the coordinates of A in ITRF1997 at epoch 2000
X(1997/2000)=
Y(1997/2000)=
Z(1997/2000)=
解:
步骤:
(1)将2012年10月10号计算年积日=282天;
(2)计算历元:2012+(282/365)=2012.7726;
(3)获取在2012.7726历元的转换参数;
\(\begin{align*}
\begin{bmatrix}T_1\\T_2\\T_3\\D\\R_1\\R_2\\R_3
\end{bmatrix}_{2012.7726}
&=
\begin{bmatrix}
T_1\\T_2\\T_3\\D\\R_1\\R_2\\R_3
\end{bmatrix}_{1997.0}
+(2012.7726-1997.0)\begin{bmatrix}
\dot{T_1}\\\dot{T_2}\\\dot{T_3}\\\dot{D}\\\dot{R_1}\\\dot{R_2}\\\dot{R_3}
\end{bmatrix}_{1997.0}\\
&=
\begin{bmatrix}
0.0067\\0.0061\\-0.0185\\1.55\\0\\0\\0
\end{bmatrix}
+(2012.7726-1997.0)\begin{bmatrix}
0\\-0.0006\\-0.0014\\0.01\\0\\0\\0.02
\end{bmatrix}\\
&=
\begin{bmatrix}
0.0067\\-0.0034\\-0.0406\\1.7077\\0\\0\\0.3155
\end{bmatrix}
\end{align*}\)
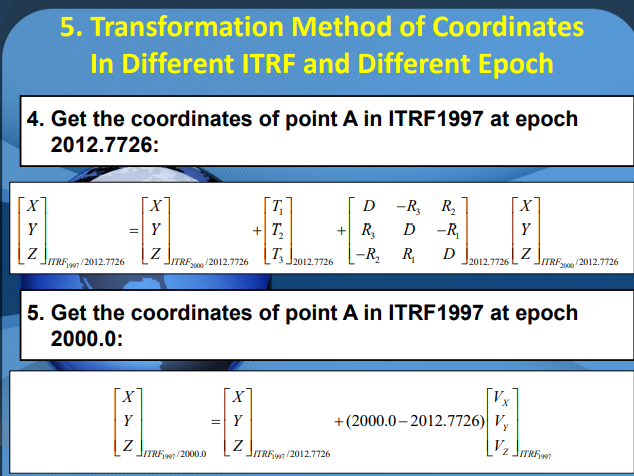
(4)获得点A在ITRF1997框架内2012.7726历元的坐标
\(\begin{align*}
\begin{bmatrix}
X \\ Y \\ Z
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997}/2012.7726}
&=\begin{bmatrix}
X \\ Y \\ Z
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{2000.0}/2012.7726}+\begin{bmatrix}
T_1 \\ T_2 \\ T_3
\end{bmatrix}_{2012.7726}+\begin{bmatrix}
D & -R_3 & R_2 \\
R_3 & D & -R_1 \\
-R_2 & R_1 & D
\end{bmatrix}_{2012.7726}\begin{bmatrix}
X \\ Y \\ Z
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{2000}/2012.7726}\\
&=\begin{bmatrix}
2 \\ 3 \\ 5
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{2000.0}/2012.7726}+\begin{bmatrix}
0.0067 \\ -0.0034 \\ -0.0406
\end{bmatrix}_{2012.7726}+\begin{bmatrix}
1.7077 & -0.3155 & 0 \\
0.3155 & 1.7077 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 1.7077
\end{bmatrix}_{2012.7726}\begin{bmatrix}
2 \\ 3 \\ 5
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{2000}/2012.7726}\\
&=\begin{bmatrix}
4.4756\\
8.7507\\
13.4979
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997.0}/2012.7726}
\end{align*}\)
(5)获得点A在ITRF1997框架内2000.0历元的坐标
\(\begin{align*}
\begin{bmatrix}
X \\ Y \\ Z
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997.0}/2000}
&=\begin{bmatrix}
X \\ Y \\ Z
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997.0}/2012.7726}+(2000-2012.7726)\begin{bmatrix}
V_X\\V_Y\\V_Z
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997}}\\
&=\begin{bmatrix}
4.4756\\
8.7507\\
13.4979
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997.0}/2012.7726}+(2000-2012.7726)\begin{bmatrix}
0.002\\0.001\\0.003
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997}}\\
&=\begin{bmatrix}
4.4501\\8.7379\\13.4596
\end{bmatrix}_{ITRF_{1997.0}/2000}
\end{align*}\)
参考课件:
Use both files FILE 1 and FILE 2 (observation and navigation files) in the next page, please
FILE 1
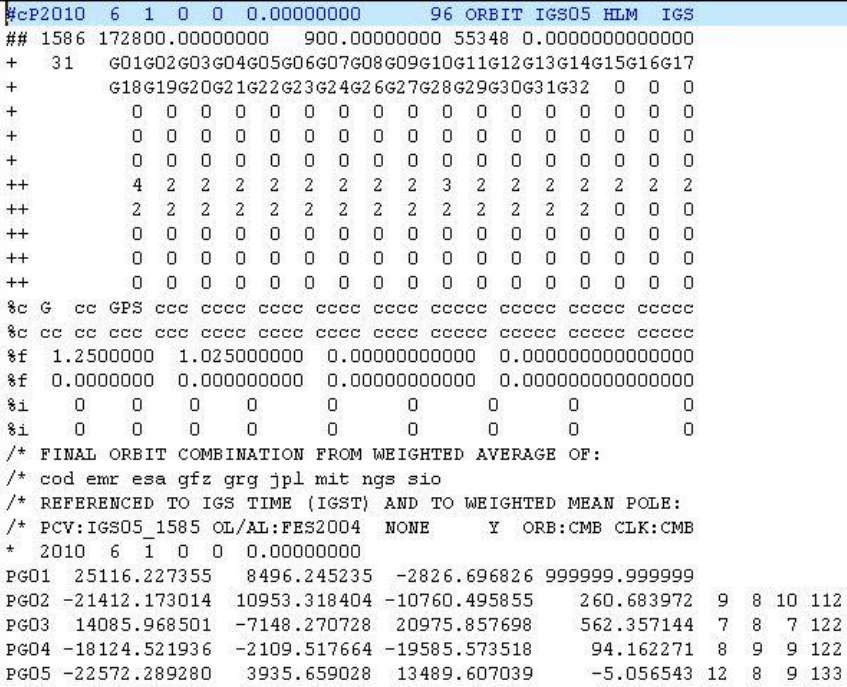 FILE 2
FILE 2
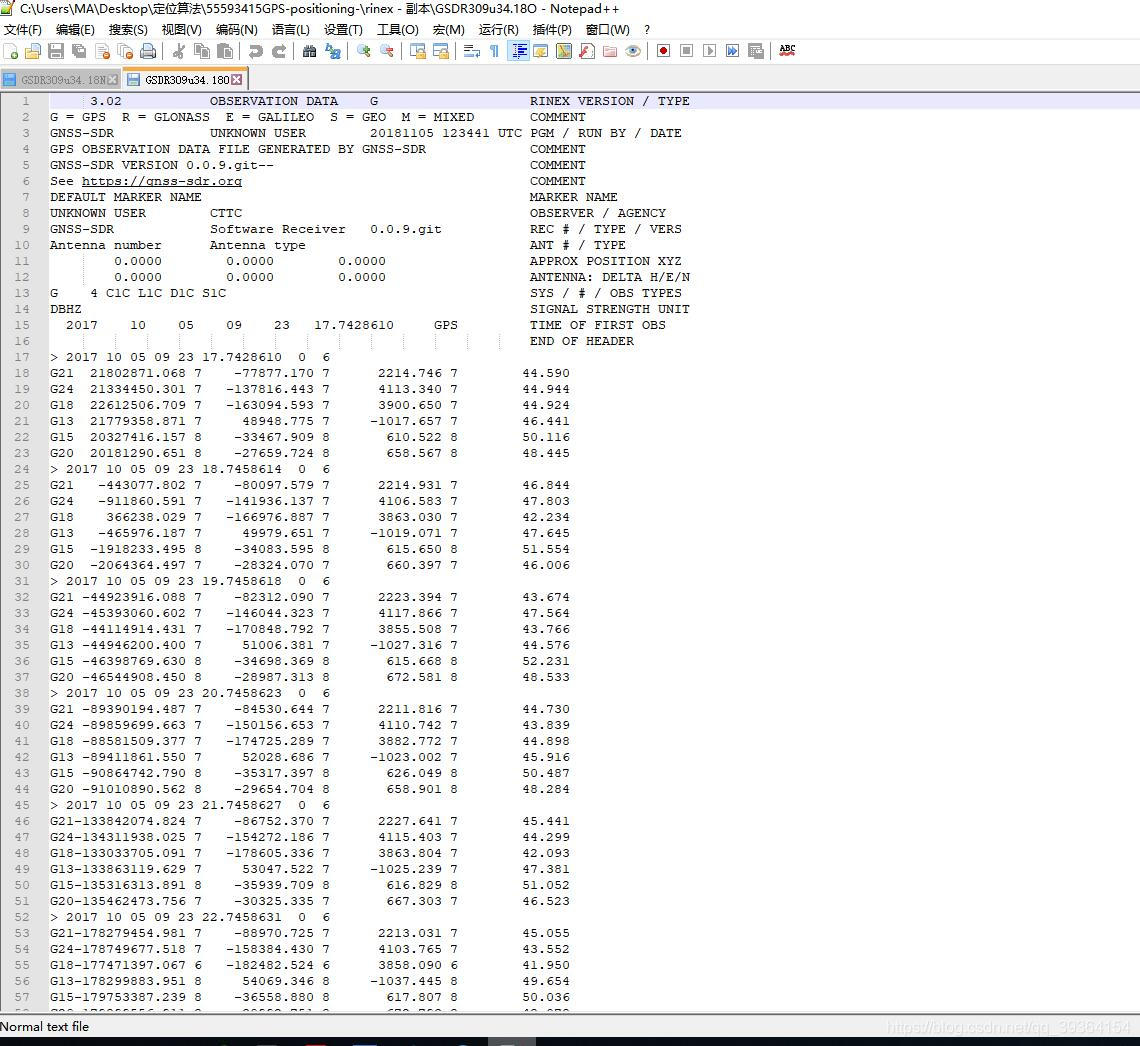 NAVIGATION FILE
NAVIGATION FILE

(1) Find out the satellite orbit coordinates of GO1 on the X component and the number of bad satellites from the FILE 1;
(2)What kinds of satellite are observed?
(3)What is the C1 observation value of the R19 satellite at the first epoch in the FILE 2?
答:(1)25116.237355列为x项,单位为千米;卫星G01钟差超限,是 bad satellite;(2)文件1观测到了GPS卫星,共31颗;文件2观测到了GPS卫星和GLONASS卫星。(3)文件2中第一历元R19的C1观测值是21640154.859
Note: sp3 格式说明
- 第1行的第1列为版本,这里为a,后续高版本将依次按照字母顺序命名;第3列P表示坐标,注意有的版本包含速率的时候该字符为V,接着为时间(4-7列(年)、9-10列(月)、12-13列(日)、15-16列(时)、18-19列(分)、21-31列(秒));96代表历元数(33-39列);IGS00代表坐标系统(47-51列)。
- 第2行1148表示GPS周(4-7列);0.00000000周内秒(9-23列);900.00000000历元间隔(25-38列);52280儒略日(40-44列);0.0000000000000儒略日小数秒(46-60)。
- 第3行到第7行为卫星编码,其中第3行的28为卫星数(5-6列)。第8行至第12行为精度。
- 13至18行,19到22行为注释行。
- 23行观测历元:4-7列(年)、9-10列(月)、12-13列(日)、15-16列(时)、18-19列(分)、21-31列(秒)。
- 24行第一列为P(位置,单位km),2-4列卫星号。5-18列x坐标,19-32列y坐标,33-46列z坐标。(注意当第一列标识为V表示速率时候,其单位为分米/秒(dm/sec))。47-60列 钟差(单位微妙,当第一列标识为V时表示时间变化率,其单位为毫秒/秒(microsec/sec))。注意如果数据行第75列有‘E’字符,表示卫星坐标或者钟记录存在事件。